The Basic Frame of SDRAM & DDR
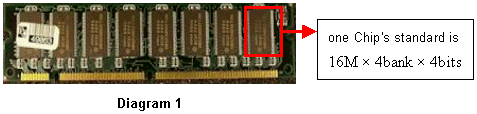
Before explain the SDRAM & DDR, we first explain the frame of memory. Usually when you handing a piece (or one root) of memory, you can see the chip's specification of this memory from which listed in the standard of the memory. For example: 16m * 4bank * 4bits.
This 16m * 4bank * 4bits indicates: 16 x 4 x 4 = 256mbits = 32MB, that is one Chip's capacity is 32MB. The memory showed in above diagram has 8 Chips( presume this memory is single bank side), so this piece of memory's capacity is 32 x 8 = 256MB.
4 bank means there is 4 banks in each chip. What is called bank can be regarded as there is 4 bank(or store) in each chip, each bank can store up to 16M words capacity and word is the store unit of bank.
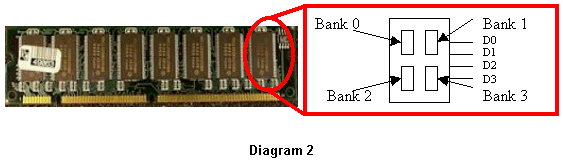
(The denotation of "4bits" is: there are 4 pieces of data line D0~D3 (as diagram 2). So the memory showed in above diagram has 8 chips and each chips has 4 data lines, then it has 8*4=32 data lines i.e. 32bit. Therefore from the standard of one piece (or one root) of memory you can see this memory how many bit that is how many data lines totally. At present North Bridge, the chip connect to memory mostly has 64bit, so manufacturers recently release memory in which the total data lines are all designed to be 64 pieces(64bit). If the business is with like above memory particle(chip), the manufacturer will produce a 512MB memory using 16 chips with 8 chips each side.
Fortunately, the value of these registers can be modified through some special methods, like battery learning, which is an effective way to normalize the rechargeable time and capacity of battery by modifying the values of battery capacity register and battery conditions register to correct the existing errors in registers.
1. SDRAM:
SDRAM is a kind of DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory), Its main characteristic lies in "Synchronous", that is the affiliation by micro processor in the memory module causes the memory running pulse synchronous with the CPU, so that the data can be transmitted more quickly. Dynamic means the data existed in the memory will lose by the lack of electricity when the PC shut down or freezing. And the STR in ACPI (Suspend to RAM, S3 module) is the module that reserving the recent situation of system into RAM. At this moment the power of peripheral equipment is almost all off aside from RAM. So the data can be preserved. But if unfortunately the power is all down, the data stored in the RAM is also lose. Even if restart the wwPC, it is impossible to revert the previous STR status. SDRAM at present, the standard has PC 100 and the PC133. What is called 100 and 133 refers to the time pulse of memory is 100Mhz and 133Mhz.
At present SDRAM has divides into two memory module: 168 pin (3.3volt) and 144 pin (3.3volt). 168 pin module is for Desktop, but 144 pin module is for notebook.
2. DDR SDRAM:
DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory). It uses the Extends technique of SDRAM.
At present, DDR SRDAM can often be seen in two standards: PC1600 and PC2100. In the fact the PC 1600's frequency is also 100Mhz (the same to previous PC-100). The reason why it is called PC1600 is because:
64bit x 100Mhz x 2=1600 MB/Sec,
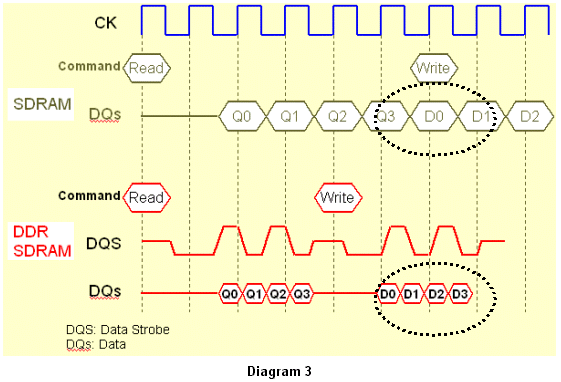
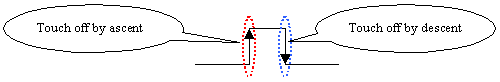
The "2" is because it is DDR. It is touched off by both ascent and descent of CLOCK i.e. it reads data 2 times in one CLOCK course. So multiplying "2" is necessary.
And the PC 2100's frequency is 133 Mhz (the same to previous PC-133). The reason why it is called PC 2100 is because:
64bit x 133Mhz x 2=2100 MB/Sec
. The "2" is also because it is DDR and be touched off by both ascent and descent of CLOCK.
The following diagram is the time-chart of SDRAM and DDR:
P.S. The ascent of CLOCK (CK) refers to the CLOCK turn from low-level to high-level. And the touch off by ascent means reading the data just when the point the CLOCK turn from low-level to high-level. Inversely, the descent of CLOCK refers to the CLOCK turn from high-level to low-level.
DDR SDRAM also has divides into Desktop (184 pin, 2.5volt) and Notebook (200 pin, 2.5volt) uses.
The comparison between SDRAM and DDR:
SDRAM
Module
Frequency
Bandwidth
PC-66 DIMM
66Mhz
528 MByte/sec
PC-100 DIMM
100Mhz
800 MByte/sec
PC-133 DIMM
133Mhz
1.06 Gbyte/Sec
DDR SDRAM
Module
Frequency
Bandwidth
DDR 200(PC-1600)
100Mhz
1600 MByte/sec
DDR 266(PC-2100)
133Mhz
2.121 Gbyte/Sec
DDR 333(PC-2700)
166Mhz
2.66 Gbyte/Sec