| Accelerated Graphics Port |

124 Position AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
Question: What is AGP ? Answer: AGP stands for Accelerated Graphics Port. It is an interface specification specifically written to provide an interface for a high performance graphics engine at mainstream prices, especially in the area of 3D graphics. It puts a home computer in a par with a 3D workstation that could not be done before. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: How does AGP accomplish high-end 3D graphics affordable to general publics? Answer: Higher bandwidth is achieved by utilizing dedicated pipelined access to main memory for faster data transfer rate, and cost is reduced by moving graphics data to main memory. Thus allowing AGP interfaces to use system memory for texturing, z-buffering, and alpha blending avoid the heavy burden of expensive on-board graphic memory. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: Is AGP designed to be the replacement for the PCI bus? Answer: No. AGP is designed solely for the use of graphics controller, it's not intended to replace the role of the PCI interface as the general I/O interface bus. AGP is physically, logically, and electrically independent of the PCI bus. The interface uses a freshly new bus design which is not compatible with the existing bus connector. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: What operating systems are able to support AGP? Answer: So far, Microsoft has announced to support AGP bus in the future releases of both Win95(OSR2.1, VGARTD.VXD from Intel) and NT 4.0 (with Service Pack 3) operating systems. There are over one hundred companies have joined AGP Implementor Forum world wide, including many major graphics component manufacturers and software companies. Other major OS players should soon announce the support for AGP if not already. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: Is AGP another name for UMA? Answer: No. The primary purpose of AGP is to support high-end 3D graphics on a PC by utilizing system memory for 3D effects such as textures, alpha buffers, and z-buffers, while there is still a dedicated on-board frame buffer memory on the card itself. While UMA architecture is aiming to move all the on-board frame buffer memory to the system memory to reduce cost on the expensive on-board dedicated buffer memory. AGP allows for dynamic memory allocation. This means OS will be able to reclaim the system memory used for 3D effects in the AGP architecture. But as to the UMA, a portion of system memory is allocated at system boot-up, and it can not be reclaimed dynamically by the OS. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: What different features does AGP have over PCI? Answer: A comparison table below lists the differences:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: What are the Benefits of AGP? Answer:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: What's the Architecture of AGP? Answer: Figure below shows a simplified diagram of an AGP system, with peak bus bandwidths and memory usage. The bus on the right hand side of the Chipset, between the memory controller and system memory is typically 64 bits wide, and must be shared by CPU, graphics chip, and PCI bus. Because of the large amount of RAM support for the system memory, its clock rate is usually slower than the graphics local memory bus. The initial chip sets will support 528 MB/s peak on that system bus, but future versions may increase it. The 800 MB/s peak between local memory and the graphics chip comes from a 64-bit bus at 100 MHz as defined in a typical high performance graphics card. 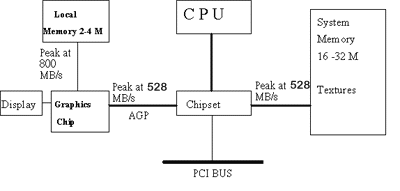
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: What's Direct Memory Execute (DIME)? Answer: The most powerful feature of AGP is the use of DIME. With DIME implemented, AGP graphics chips have the capability to access main memory directly (called DIME, Direct Memory Execute) for the complex operation of texture-mapping. Without the DIME, most PCI-generation graphics controllers can only do texture from local graphics memory attached directly to the graphics chip. This would require an extra copying from system memory to CPU then through chipset to local memory via PCI bus for every data transfer. However, some initial AGP graphics chips available on the market today may only implement PCI-like bus mastering, or maybe none at all. AGP bus will provide faster transfer rates, but they will have to transfer the entire texture map to their local memory via AGP, then re-access the texture from that local RAM to map individually. 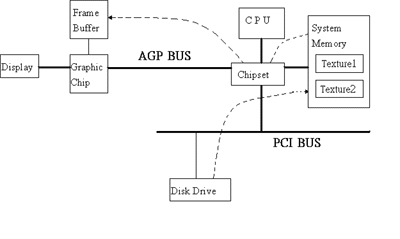
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: How to compare AGP performance with a tradition VGA display card? Answer: AGP cards should be tested like any other graphics cards except, for a more accurate test measurements of AGP you should do a test specifying a large amount of textures (>8MB). Since 3D is the area that really differentiate a AGP display cards with a traditional VGA display card, therefore a more suitable test program is the one that does a lot of 3D scenario measurements. Current version of Winbench 3D now has a scene with large textures for a more realistic test environment. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: What are the performance ratings for AGP? Answer: Comparison tests among PCI based VGA cards and AGP VGA cards are provided below:
Testing environment :
- M/B: (1)KN97-X with Intel Pentium II MMX - 266 Mhz CPU
with ATI 3D RAGE II VGA
(2)LX97 with Intel Pentium II MMX - 266 Mhz CPU
with ATI 3D RAGE PRO AGP-133 VGA
- 32MB (EDO 32MB * 1), Internal 512KB Cache
- Adaptec AHA-2940UW SCSI Controller
- Seagate ST32171W
- Logitech Serial Mouse
3D Winbench 97 for Windows 95
Direct 3D Benchmark
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question: Where can I obtain more information on AGP? Answer: Following are links to other WEB sites to obtain more information on AGP: AGP Implementors Forum: list of companies to implement AGP architecture, and also the newest AGP HW/SW news. Intel WEB site: AGP hardware overview. Microsoft WEB site: Information on Microsoft OS support for AGP. Diamond AGP white paper. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||